REVS: Unlearning Sensitive Information in Language Models via Rank Editing in the Vocabulary Space
Tomer Ashuach, Martin Tutek, and Yonatan Belinkov
In Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025, 2024
Language models (LMs) risk inadvertently memorizing and divulging sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII) seen in training data, causing privacy concerns. Current approaches to address this issue involve costly dataset scrubbing, or model filtering through unlearning and model editing, which can be bypassed through extraction attacks. We propose REVS, a novel non-gradient-based method for unlearning sensitive information from LMs. REVS identifies and modifies a small subset of neurons relevant for constituent tokens that form sensitive information. To adequately evaluate our method on truly sensitive information, we curate three datasets: email and URL datasets naturally memorized by the models, and a synthetic social security number dataset that we tune the models to memorize. Compared to other methods, REVS demonstrates superior performance in unlearning sensitive information and robustness to extraction attacks, while retaining underlying model integrity.
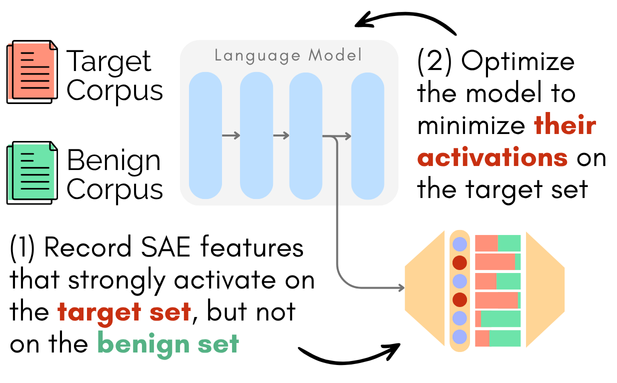 CRISP: Persistent Concept Unlearning via Sparse AutoencodersarXiv preprint arXiv:2508.13650, 2025As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, the need to selectively remove unwanted knowledge while preserving model utility has become paramount. Recent work has explored sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to perform precise interventions on monosemantic features. However, most SAE-based methods operate at inference time, which does not create persistent changes in the model’s parameters. Such interventions can be bypassed or reversed by malicious actors with parameter access. We introduce CRISP, a parameter-efficient method for persistent concept unlearning using SAEs. CRISP automatically identifies salient SAE features across multiple layers and suppresses their activations. We experiment with two LLMs and show that our method outperforms prior approaches on safety-critical unlearning tasks from the WMDP benchmark, successfully removing harmful knowledge while preserving general and in-domain capabilities. Feature-level analysis reveals that CRISP achieves semantically coherent separation between target and benign concepts, allowing precise suppression of the target features.
CRISP: Persistent Concept Unlearning via Sparse AutoencodersarXiv preprint arXiv:2508.13650, 2025As large language models (LLMs) are increasingly deployed in real-world applications, the need to selectively remove unwanted knowledge while preserving model utility has become paramount. Recent work has explored sparse autoencoders (SAEs) to perform precise interventions on monosemantic features. However, most SAE-based methods operate at inference time, which does not create persistent changes in the model’s parameters. Such interventions can be bypassed or reversed by malicious actors with parameter access. We introduce CRISP, a parameter-efficient method for persistent concept unlearning using SAEs. CRISP automatically identifies salient SAE features across multiple layers and suppresses their activations. We experiment with two LLMs and show that our method outperforms prior approaches on safety-critical unlearning tasks from the WMDP benchmark, successfully removing harmful knowledge while preserving general and in-domain capabilities. Feature-level analysis reveals that CRISP achieves semantically coherent separation between target and benign concepts, allowing precise suppression of the target features.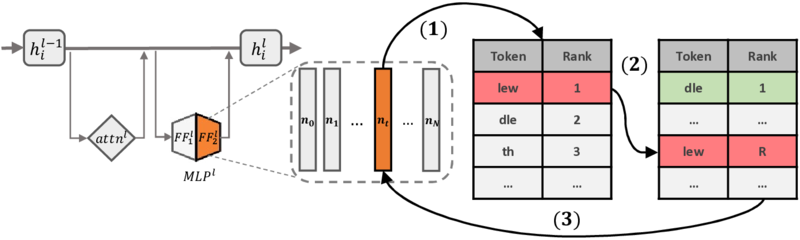 REVS: Unlearning Sensitive Information in Language Models via Rank Editing in the Vocabulary SpaceIn Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025, 2024Language models (LMs) risk inadvertently memorizing and divulging sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII) seen in training data, causing privacy concerns. Current approaches to address this issue involve costly dataset scrubbing, or model filtering through unlearning and model editing, which can be bypassed through extraction attacks. We propose REVS, a novel non-gradient-based method for unlearning sensitive information from LMs. REVS identifies and modifies a small subset of neurons relevant for constituent tokens that form sensitive information. To adequately evaluate our method on truly sensitive information, we curate three datasets: email and URL datasets naturally memorized by the models, and a synthetic social security number dataset that we tune the models to memorize. Compared to other methods, REVS demonstrates superior performance in unlearning sensitive information and robustness to extraction attacks, while retaining underlying model integrity.
REVS: Unlearning Sensitive Information in Language Models via Rank Editing in the Vocabulary SpaceIn Findings of the Association for Computational Linguistics: ACL 2025, 2024Language models (LMs) risk inadvertently memorizing and divulging sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII) seen in training data, causing privacy concerns. Current approaches to address this issue involve costly dataset scrubbing, or model filtering through unlearning and model editing, which can be bypassed through extraction attacks. We propose REVS, a novel non-gradient-based method for unlearning sensitive information from LMs. REVS identifies and modifies a small subset of neurons relevant for constituent tokens that form sensitive information. To adequately evaluate our method on truly sensitive information, we curate three datasets: email and URL datasets naturally memorized by the models, and a synthetic social security number dataset that we tune the models to memorize. Compared to other methods, REVS demonstrates superior performance in unlearning sensitive information and robustness to extraction attacks, while retaining underlying model integrity.